MIB Issue Hightlights
Beginning in 2022, we will be highlighting different articles from each issue. We will provide a brief Q&A from the authors about the article that produces the cover image as well as highlight an open access article from the same issue.
COVER IMAGE ARTICLE
“CXCR4-Directed PET/CT with [68Ga]Pentixafor in Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Comparison with [18F]FDG PET/CT” by Zhenying Chen et al. [ Read abstract ]
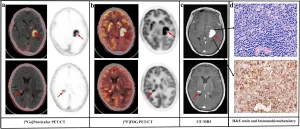
A 68-year-old man (patient #7) with newly diagnosed CNSL. Both [68 Ga]Pentixafor (a) and [18F]FDG (b) PET/CT showed two positive lesions (red arrows), which were consistent with CE-MRI (c). The H&E stain and immunohistochemistry showed CXCR4 overexpression in the tumor cells (d).
What is the purpose of your research?
C-X-C-motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) is a 7-transmembrane G-coupled receptor belonging to the chemokine receptor family, and CXCR4 overexpression is well-documented in various lymphomas. [68Ga]Pentixafor, as a specific CXCR4-targeted PET imaging agent, showed low nonspecific background accumulation in the normal brain. Therefore, our research is to evaluate the value of [68Ga]Pentixafor PET/CT for the detection of lesions in the patients with central nervous system lymphoma (CNSL).
What is innovative about your research?
The application experience of [68Ga]Pentixafor PET scan is still limited to assessing the response of CNSL lesions to chemotherapy and detecting the recurrence of CNSL. In our study, we evaluated [68Ga]Pentixafor PET/CT to detect CNSL lesions before chemotherapy, assess the lesions during treatment, and the detect the recurrent lesions. Moreover, the comparison of the efficacy of [18F]FDG and [68Ga]Pentixafor for detecting CNSL lesions was performed which was not reported in the previous studies.
Can you describe your conclusions?
Our research demonstrated that [68Ga]Pentixafor PET/CT and MRI were comparable in accurately detecting CNSL lesions. [68Ga]Pentixafor PET imaging, with excellent tumor-to-background contrast, might be a more promising agent for the detection of lesions in CNSL patients than [18F]FDG PET/CT. [68Ga]Pentixafor PET/CT may be helpful for the positioning of stereotactic biopsy.
What are the next steps for your research?
The next steps for our research is to investigate the value of [68Ga]Pentixafor PET for evaluating the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) in patients with CNSL.
If you are the senior author, can you tell me something about the first (trainee) author?
The first author, Dr. Chen (full name, Zhenying Chen; e-mail, chenzhenying726@foxmail.com), is an attending physician of the nuclear medicine department. She has been engaged in the research of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging for 8 years. She has published some papers in Mol Imaging Biol, Clin Nucl Med, Ann Nucl Med, and Chinese Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
COVER IMAGE ARTICLE
“Clinical Utility of F-18 Labeled Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) for Primary Staging in Lung Adenocarcinoma: a Prospective Study” by Youcai Li et al. [ Read abstract ]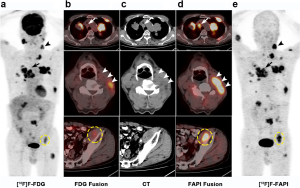 A 66-year-old man with known lung adenocarcinoma underwent [18F]F-FDG PET/CT for initial staging. (a) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of [18F]F-FDG PET images. (b) [18F]F-FDG PET/CT showed multiple lymph node metastases in the mediastinum (arrow) and neck (arrow head) regions, muscle metastasis in the iliopsoas muscle (circle), with mild-to-moderate [18F]F-FDG activity in these lesions (SUVmax = 1.71–5.85). (c) Images of CT. (d) [18F]F-FAPI PET/CT showed much higher SUVmax in the enlarged lymph nodes in mediastinum (arrow) and neck (arrow head), and in the iliopsoas muscle (circle) (SUVmax = 9.76–11.63). (e) MIP of [18F]F-FAPI PET images.
A 66-year-old man with known lung adenocarcinoma underwent [18F]F-FDG PET/CT for initial staging. (a) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of [18F]F-FDG PET images. (b) [18F]F-FDG PET/CT showed multiple lymph node metastases in the mediastinum (arrow) and neck (arrow head) regions, muscle metastasis in the iliopsoas muscle (circle), with mild-to-moderate [18F]F-FDG activity in these lesions (SUVmax = 1.71–5.85). (c) Images of CT. (d) [18F]F-FAPI PET/CT showed much higher SUVmax in the enlarged lymph nodes in mediastinum (arrow) and neck (arrow head), and in the iliopsoas muscle (circle) (SUVmax = 9.76–11.63). (e) MIP of [18F]F-FAPI PET images.COVER IMAGE ARTICLE
“124I-Iodo-DPA-713 Positron Emission Tomography in a Hamster Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection” by Camilo A. Ruiz-Bedoya et al. [ Read abstract ]
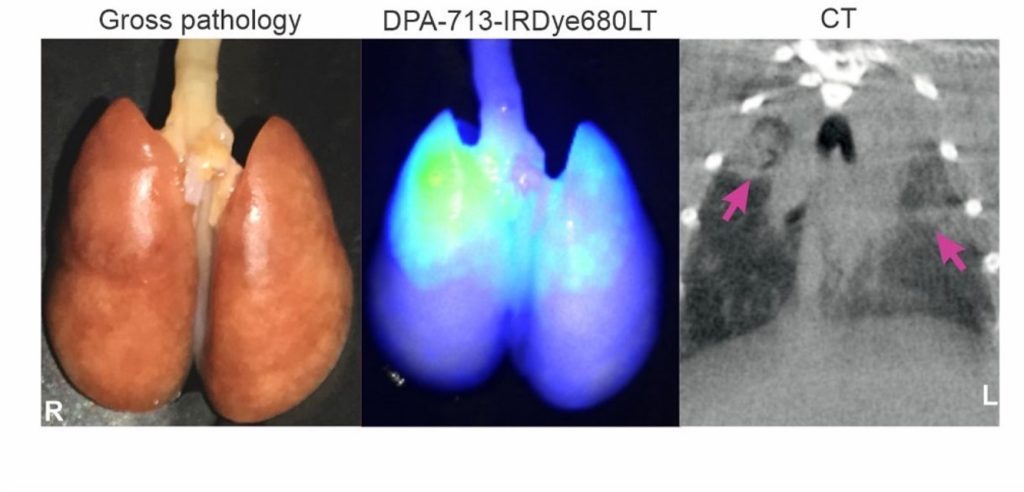
Pulmonary 124 PET/CT of SARS-CoV-2-infected hamsters. DPA-713-IRDye680LT fluorescence co-localizes with the diseased lung.
What is the purpose of your research?
We have previously demonstrated that radioiodinated DPA-713 (124I-Iodo-DPA-713), a small molecule targetting TSPO, specifically accumulates in activated macrophages and phagocytic cells in the lungs of animals with pulmonary tuberculosis. Given that lung monocytes and macrophages are involved with the pathogenesis of COVID-19, we wanted to investigate if 124I-Iodo-DPA-713 PET could be used to detect and quantify lung disease in a hamster model of Covid-19. In collaboration with several investigators at Johns Hopkins, we had also recently demonstrated differences in lung pathology between male and female Golden Syrian hamsters, which mirred humn disease. Therefore, we also aimed to monitor sex differences in the pulmonary immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
What is innovative about your research?
Since we initiated this project soon after COVID-19 hit, we had to quickly and effectively innovate across multiple areas to be able to conduct these studies. For instance, here we present the development of a transparent and sealed biocontainment cell (developed in-house), compliant with BSL-3 containment and capable of sustaining live SARS-CoV-2-infected animals outside a BSL-3 facility during imaging. We also report the use of a custom-built lung segmentation tool for generating volumes of interest in hamster lung by CT. Lastly, these technological advances allowed us to assess sex differences in local lung disease using 124I-Iodo-DPA-713 PET/CT imaging in SARS-CoV-2 infected animals.
Can you describe your conclusions?
In this study, we performed pulmonary 124I-Iodo-DPA-713 PET/CT imaging in SARS-CoV-2-infected golden Syrian hamsters at the peak of inflammatory lung disease (7 days post-infection). Quantitative CT analysis demonstrated worse pulmonary disease in males than females. Increased 124I-Iodo-DPA-713 uptake co-localized with the pneumonic lesions, with higher levels also being noted in male compared to female hamsters. DPA-713-IRDye680LT, a fluorescent dye analogous to 124I-Iodo-DPA-713, also localized to the pneumonic lesions. Flow cytometry demonstrated a higher percentage of myeloid and CD11b+ cells in male versus female lung tissues. Altogether, these results indicate that 124I-Iodo-DPA-713 can be used to non-invasively monitor SARS-CoV-2 – associated pulmonary inflammation.
What are the next steps for your research?
Thanks to the development of a new protocol to image SARS-CoV-2-infected animals, and the knowledge we acquired in using this animal model, we are now able to develop and characterize novel PET-tracers in SARS-CoV-2-infected animals. We have several collaborations ongoing and are currently using this technology to further characterize mechanisms of pathogenesis to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
OPEN ACCESS ARTICLE
“Molecular Imaging Reveals a High Degree of Cross-Seeding of Spontaneous Metastases in a Novel Mouse Model of Synchronous Bilateral Breast Cancer” by Shirley Liu, et al. [ Read article ]
Patients with synchronous bilateral breast cancer show higher rates of metastases and lower survival rates compared to women with unilateral breast cancer. This study uses molecular imaging to visualize metastases patterns to help optimize treatment planning and understand treatment resistance.
